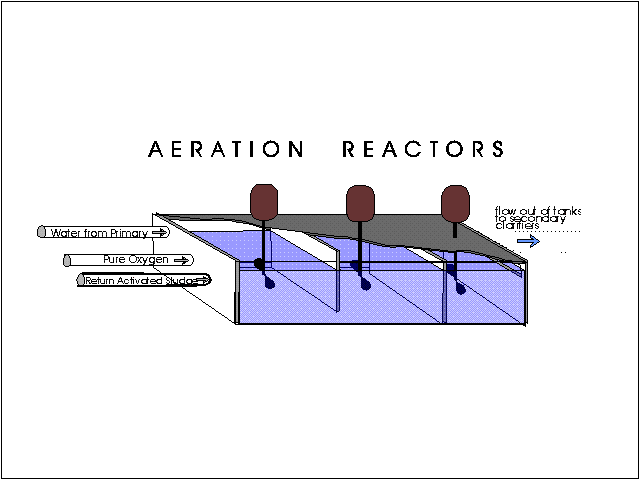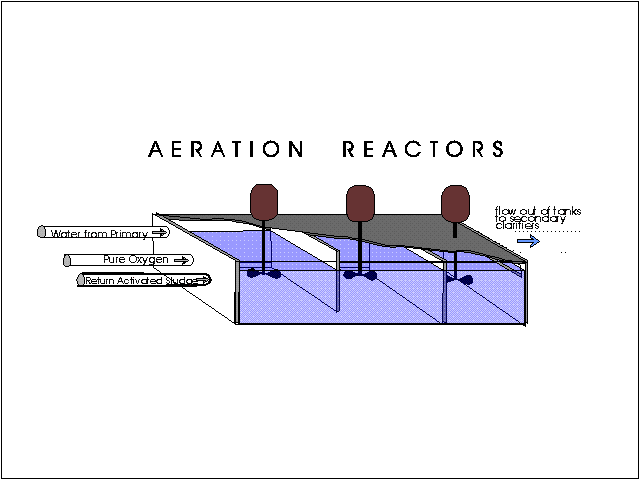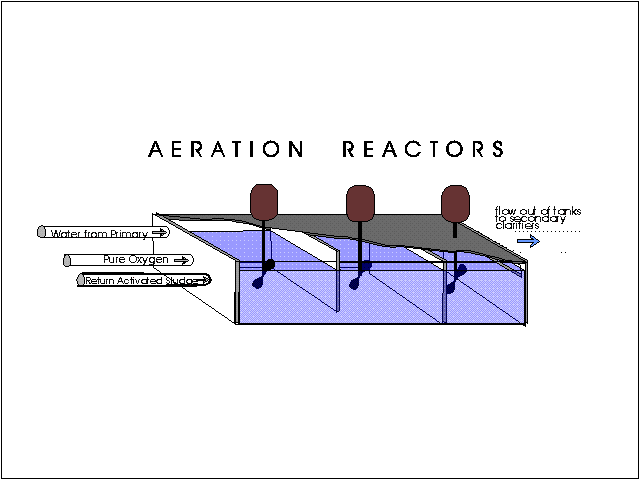



Advantages of extended Aeration System:
Plants are easy to operate, as the management of operation is for a maximum of two or three hours per day.
Extended aeration processes are often better at handling organic loading and flow fluctuations, as there is a greater detention time for the...
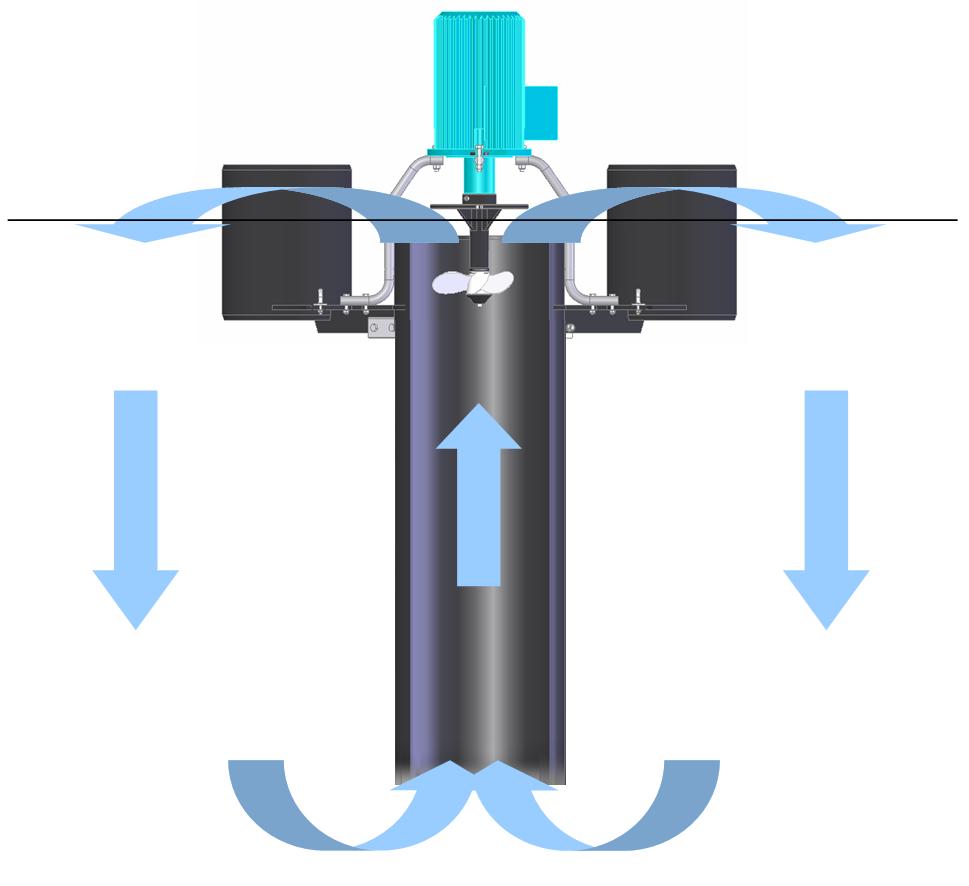
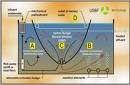
Mechanical Aerator
surface aerator
Type of Mechanical Aerators
Mechanical aerators are of two general types; surface aerators and turbine aerators.
Surface aerators consist of submerged or partially submerged impellers, which are centrally mounted in the aeration tank. Surface aerators agitate the wastewater...

AERATION
Aeration serves three important functions :
Mixing the returned sludge with effluent from primary treatment,
Keeping the activated sludge in suspension, and
Supplying the oxygen to the biochemical reactions necessary for the stabilization of the wastewater.
The theoretical oxygen requirement...

ROTATING BIOLOGICAL CONTACTOR
The rotating biological contactor (RBC) has been used in Europe for many years to treat both municipal and industrial waste waters. RBC’s produce a high quality effluent. RBC’s are fixed-film reactors similar to bio filters in that organisms are attached to support media. The support...

TYPES OF TRICKLING FILTERS
The Trickling filters are classified based on hydraulic or organic loading, as low rate trickling filter (LRTF), high rate trickling filter (HRTF) and Roughing Filter.
1 Low Rate Trickling Filter (LRTF)
The standard rate or Low rate trickling filters (LRTF) are relatively simple treatment units...

ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF TRICKLING FILTER
Advantages of Trickling filtration plant
Simple and reliable process that is suitable in areas where large tracts of land are not available for a WSP treatment system
Effective in treating high concentrations of organic material depending on the type of media used;
Very efficient in removal of...
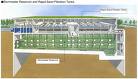
SECONDARY TREATMENT
SOLIDS IN SEWAGE
The solids present in the sewage are of two types viz.,
Organic solids, and
Inorganic solids.
Organic solids are the substances derived from living things like produces from plant and animal. Examples of organic solids are carbohydrate, protein, and fat. The organic solids...
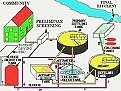
Sewage Treatment Process
Waste Water Treatment Process
1.Physical Water Treatment Operations
In the physical unit operations physical forces are utilized in some water treatment units for the removal of solid contaminants. The physical unit water treatment operations are:
water treatment Screening
water treatment...
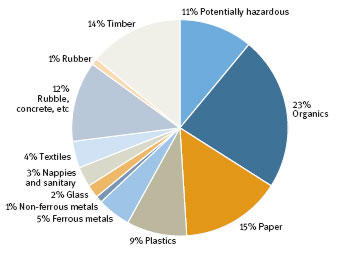
Waste Water Treatment Composition
NEED FOR WASTEWATER TREATMENT
Sewage is composed of 99.7 to 99.9% of liquid depending upon the per-capita water supply rate; more per-capita water supply means more percentage of liquid content in sewage. Sewage contains only 0.1 to 0.3% of solids, but these solids are responsible for all kinds of...






 LIKE TO GET UPDATES
LIKE TO GET UPDATES  TO GET EXPERT GUIDE
TO GET EXPERT GUIDE