

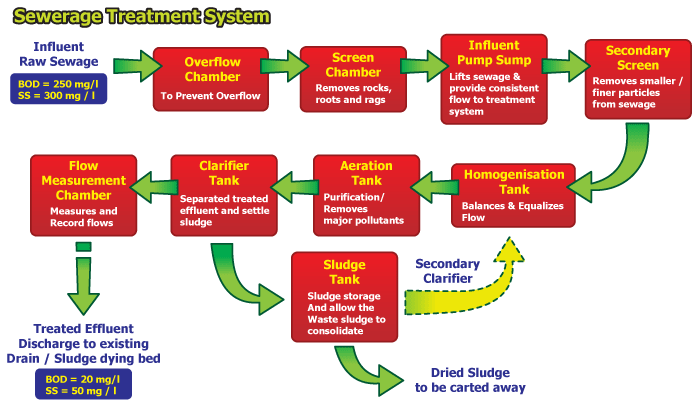
Extended Aeration System
The extended aeration process is one of the modifications of the ASP. It is a complete mix system and provides biological treatment for the removal of biodegradable organic wastes under aerobic conditions. Air may be supplied by mechanical or diffused aeration to provide the oxygen required to sustain the aerobic biological process. Mixing must be provided by aeration to maintain the microbial organisms in contact with the dissolved organics. Since there is complete stabilization is occurred in the aeration tank, there is no need for separate sludge digester. Further primary settling tank is also omitted and settleble organic solids are also allowed to settle in the aeration tank due to long detention time in the aeration tank. Process flow diagram of extended aeration system is furnished below
The treatment steps are as follows:
- Wastewater after removal of floating solids and grits and flow equalization in an equalization tank. In the equalization tank the wastewater is constantly mixed to keep the solids in suspension with coarse bubble diffusers. The wastewater is withdrawn to a pump well and pumped at uniform rate to the aeration tank. The equalization tank is provided in duplicate to facilitate cleaning when needed.
- In aeration tank the wastewater is mixed with activated sludge and oxygen is provided to the microorganisms through diffused aeration. The waste water is retained in the aeration tank for 15 hours in order to decompose organic matter present in the waste water.
- The mixed liquor then flows to a secondary settling tank (SST) where most microorganisms settle to the bottom of the settling tank along with sludge,
- A portion of the sludge (equal to 50% of the wastewater flow) is pumped to the aeration tank to mix with incoming wastewater and provide sufficient microorganisms as return activated sludge (RAS).
- The clarified wastewater from the SST then flows over V-notches into the effluent launder and into an effluent storage tank for further treatment and disposal.
Advantages of extended aeration system:
- Plants are easy to operate, as the management of operation is for a maximum of two or three hours per day.
- Extended aeration processes are often better at handling organic loading and flow fluctuations, as there is a greater detention time for the nutrients to be assimilated by microbes.
- Systems are odor free, can be installed in most locations, have a relatively small footprint, and can be landscaped to match the surrounding area.
- Extended aeration systems have a relatively low sludge yield due to long sludge ages, can be designed to provide nitrification, and do not require a primary clarifier. .
Disadvantages of extended aeration system:
- Extended aeration plants do not achieve denitrification or phosphorus removal without additional unit processes.
- Flexibility is limited to adapt to changing effluent requirements resulting from regulatory changes.
- A longer aeration period and hence requires more energy.
- Skilled personnel are required for the operation and control of return sludge and maintenance of MLSS concentration in the aeration tank.
4 Responses to “Extended Aeration System”
Leave a Reply






 LIKE TO GET UPDATES
LIKE TO GET UPDATES  TO GET EXPERT GUIDE
TO GET EXPERT GUIDE
Hello,
We are the contracting co. now would like to engage in the STP Plant installations in India. If any of the Companies are interested to work with us in india, you can contact me.
Regards
dear concern,
have a look into our site and kindly revert back to me of your interest
THERE ARE FOUR PONDS IN THE SYSTEM.
POND-1(INLET) IS EXTENDED AERATION POND.
POND-2 IS SETTLING POND.
POND-3 IS AUXILIRY SETTLING POND.
POND-4 IS FINAL TREATED POND WITH CHLORINATION
PLEASE COMMENT & GIVE ADVICE.
How wonderful that the operation of a plant is only three hours a day. I am starting an agricultural business this year and I’m getting my equipment ready. I will find a good farm wastewater aerator treatment service for this.